Downlink Angle of Departure based Positioning for Rural Macro Terrain in 5G and Beyond Network
Downlink Angle of Departure (AoD) based positioning in 5G networks is a technique used to determine the location of user equipment (UE) by analyzing the angles from which downlink signals are transmitted from the base station (gNodeB) to the UE. This method leverages the gNodeB’s ability to estimate the angles of departure of downlink signals from multiple transmit antennas, enabling the calculation of the UE’s position relative to the gNodeB. The detailed explanations of Downlink Angle of Departure (AoD) based positioning in 5G networks:
Signal Transmission and Reception: In Downlink AoD based positioning, the base station (gNodeB) transmits downlink signals to the user equipment (UE) using multiple transmit antennas. Each transmit antenna emits signals with different angles of departure, covering a range of spatial directions to reach the UE.
Angle Estimation Techniques: The UE measures the angles of departure of the downlink signals it receives from the gNodeB. This is typically achieved using signal processing techniques that analyze the phase and amplitude differences of the received signals across the UE’s antenna array. Techniques such as beamforming, spatial filtering, or maximum likelihood estimation may be employed to estimate the angles of departure accurately.
Angle of Departure Calculation: Based on the measured angles of departure from multiple antennas at the UE, the UE calculates its position relative to the gNodeB. Triangulation or multilateration techniques are commonly used for position calculation. These techniques involve using the known locations of the gNodeB antennas and the measured angles of departure to compute the UE’s position.
Antenna Configuration and Spatial Resolution: The accuracy of Downlink AoD based positioning depends on the configuration and spacing of antennas at both the gNodeB and the UE. A larger number of antennas and wider antenna spacing result in higher angular resolution, allowing for more precise angle estimation and positioning.
Positioning Accuracy and Challenges: The accuracy of Downlink AoD based positioning depends on factors such as the quality of the received signals, the presence of multipath propagation, and environmental conditions. Challenges such as signal distortion, noise, and interference can affect the accuracy of angle estimation and positioning, requiring advanced signal processing techniques and robust algorithms to mitigate these effects.
Applications and Benefits: Downlink AoD based positioning has various applications in 5G networks, including location-based services, asset tracking, indoor navigation, and emergency response. By accurately determining the positions of UEs, Downlink AoD based positioning enables the delivery of location-aware services, enhances network management capabilities, and improves overall user experience
The details of the tutorial simulation parameters is shown below:
Parameters |
Values |
|---|---|
Positioning Method |
ToA based |
Parameter Estimation Method |
ESPRIT |
Optimization Method |
Least Squrare |
Bandwidth |
30 MHz |
Subcarrier Spacing |
30 kHz |
Terrain |
Urban Macro-LoS |
Channel State Information |
Zero Forcing + Spline Interpolation |
Reference Signal |
Positioning Reference Signal (PRS) |
Simulation Type |
System Level Simulation |
Channel Normalization |
Disabled |
The tutorial will generate 5G standards compliant reference signal (PRS) which is transmitted by BS foe UE to perform measurement which inturn can be used to estimate the location of the UE. Users can generate the Wireless channel either using our tool which has one of the most exhaustive channel modelling library or use some other \(3^{rd}\) party tool such as Sionna, Quadriga to generate the channel and use it with 5G Toolkit.
Positioning Procedure
Generate the Reference Signal
Transmit the Reference Signal
Pass the Transmit Signal through Wireless Channel
Add Noise at the Receiver
Estimate the Channel at Pilot Locations
Interpolate the channel at remaining locations
Estimate the Delays (Time of arrival using the channel Estimates)
Estimate the Position using ToA estimates.
Finally, we will demonstrate the efficacy of these methods using simulation evaluation results:
Horizontal (2D) Positioning Accuracy vs SNR
Verical Positioning Accuracy vs SNR
3D Positioning Accuracy
Table of Content:
Position Estimation + K-Best Measurement Selection (Genie Aided)
Performance Analysis of Positioning Error for ToA based method
Import Libraries
Python Libraries
[1]:
# from IPython.display import display, HTML
# display(HTML("<style>.container { width:90% !important; }</style>"))
import os
os.environ["CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES"] = "-1"
os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '3'
# %matplotlib widget
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.patches as mpatches
import matplotlib as mpl
import numpy as np
import numpy.matlib
import scipy as sp
import scipy.io as spio
import scipy.constants
from scipy import interpolate
from scipy.interpolate import NearestNDInterpolator, make_interp_spline, CubicSpline, PchipInterpolator, Akima1DInterpolator
5G Toolkit Libraries
[2]:
import sys
sys.path.append("../../../")
from toolkit5G.ChannelModels import AntennaArrays, SimulationLayout, ParameterGenerator, ChannelGenerator
from toolkit5G.ResourceMapping import ResourceMapperPRS
from toolkit5G.Positioning import ToAEstimation, Position_Estimation, LeastSquareDoA
from toolkit5G.ChannelProcessing import AddNoise
Simulation Parameters
Parameters |
Values |
|---|---|
Terrain |
Rural Macro (RMa) |
Carrier Frequency |
3.6 GHz |
Subcarrier Spacing |
30 kHz |
Number of Base-station |
21 (7 sites with 3 sectors each) |
BS Deployment |
Hexagonal |
UE Dropping |
Eqaul number of UEs are dropped uniformly at random in each Hexagonal |
Number of UEs |
400 |
Bandwidth |
30 MHz (85 RBs) |
Number of RBs |
85 |
[3]:
# propTerrain = "CDL-D" # Propagation Scenario or Terrain for BS-UE links
propTerrain = "RMa" # Propagation Scenario or Terrain for BS-UE links
carrierFrequency = 3.6*10**9 # Array of two carrier frequencies in GHz
scs = 30*10**3
Nfft = 1024
nBSs = 21 # number of BSs
nUEs = 100 # number of UEs
Bandwidth = 30*10**6
numRBs = 85
print()
print("*****************************************************")
print(" Terrain: "+str(propTerrain))
print(" Number of UEs: "+str(nUEs))
print(" Number of BSs: "+str(nBSs))
print(" carrier Frequency: "+str(carrierFrequency/10**9)+" GHz")
print(" Bandwidth: "+str(Bandwidth))
print(" Number of Resource Blocks: "+str(numRBs))
print(" Subcarrier Spacing: "+str(scs))
print(" FFT Size: "+str(Nfft))
print("*****************************************************")
print()
*****************************************************
Terrain: RMa
Number of UEs: 100
Number of BSs: 21
carrier Frequency: 3.6 GHz
Bandwidth: 30000000
Number of Resource Blocks: 85
Subcarrier Spacing: 30000
FFT Size: 1024
*****************************************************
Channel Generation
Channel Parameters:
Intersite Distance: 100m
BS is deployed at 35m and UE has a random height between 0 and 1.5m.
BS Antennas Arrays:
Antenna Types: Parabolic
Number of Panels: 1
Number of Antennas: 2 Horizontally, 2 Verically
Polarization: 1 (Monopole)
UE Antennas Arrays:
Antenna Types: Hertizian (Omni)
Number of Panels: 1
Number of Antennas: 4 Horizontally, 4 Verically
Polarization: 1 (Monopole)
Mobility: No Mobility
OFDM Channel:
Carrier Phase: Disabled.
\(\text{N}_\text{fft}\): 1024
[4]:
# Antenna Array at UE side
# assuming antenna element type to be "OMNI"
# with 2 panel and 2 single polarized antenna element per panel.
ueAntArray = AntennaArrays(antennaType = "OMNI", centerFrequency = carrierFrequency,
arrayStructure = np.array([1,1,1,2,1]))
ueAntArray()
# # Radiation Pattern of Rx antenna element
# ueAntArray.displayAntennaRadiationPattern()
# Antenna Array at BS side
# assuming antenna element type to be "3GPP_38.901", a parabolic antenna
# with 4 panel and 4 single polarized antenna element per panel.
bsAntArray = AntennaArrays(antennaType = "3GPP_38.901", centerFrequency = carrierFrequency,
arrayStructure = np.array([1,1,2,16,1]))
bsAntArray()
# # Radiation Pattern of Tx antenna element
# bsAntArray[0].displayAntennaRadiationPattern()
# Layout Parameters
isd = 1732 # inter site distance
minDist = 35 # min distance between each UE and BS
ueHt = 1.5 # UE height
bsHt = 35 # BS height
bslayoutType = "Hexagonal" # BS layout type
ueDropType = "Hexagonal" # UE drop type
htDist = "equal" # UE height distribution
ueDist = "equal" # UE Distribution per site
nSectorsPerSite = 3 # number of sectors per site
maxNumFloors = 1 # Max number of floors in an indoor object
minNumFloors = 1 # Min number of floors in an indoor object
heightOfRoom = 3 # height of room or ceiling in meters
indoorUEfract = 0.5 # Fraction of UEs located indoor
lengthOfIndoorObject = 3 # length of indoor object typically having rectangular geometry
widthOfIndoorObject = 3 # width of indoor object
forceLOS = True # boolen flag if true forces every link to be in LOS state
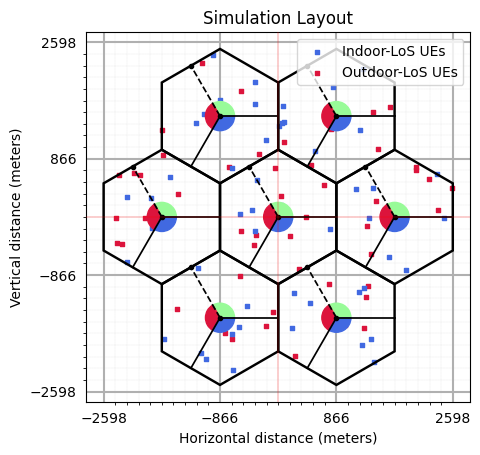
# simulation layout object
simLayoutObj = SimulationLayout(numOfBS = nBSs,
numOfUE = nUEs,
heightOfBS = bsHt,
heightOfUE = ueHt,
ISD = isd,
layoutType = bslayoutType,
ueDropMethod = ueDropType,
UEdistibution = ueDist,
UEheightDistribution = htDist,
numOfSectorsPerSite = nSectorsPerSite,
ueRoute = None)
simLayoutObj(terrain = propTerrain,
carrierFreq = carrierFrequency,
ueAntennaArray = ueAntArray,
bsAntennaArray = bsAntArray,
indoorUEfraction = indoorUEfract,
lengthOfIndoorObject = lengthOfIndoorObject,
widthOfIndoorObject = widthOfIndoorObject,
forceLOS = forceLOS)
# displaying the topology of simulation layout
fig, ax = simLayoutObj.display2DTopology()
paramGen = simLayoutObj.getParameterGenerator()
# paramGen.displayClusters((0,0,0), rayIndex = 0)
channel = paramGen.getChannel()
Hf = channel.ofdm(scs, Nfft)[0]
Nt = bsAntArray.numAntennas # Number of BS Antennas
Nr = ueAntArray.numAntennas
dBP (min, max): 3958.406982421875, 3958.406982421875
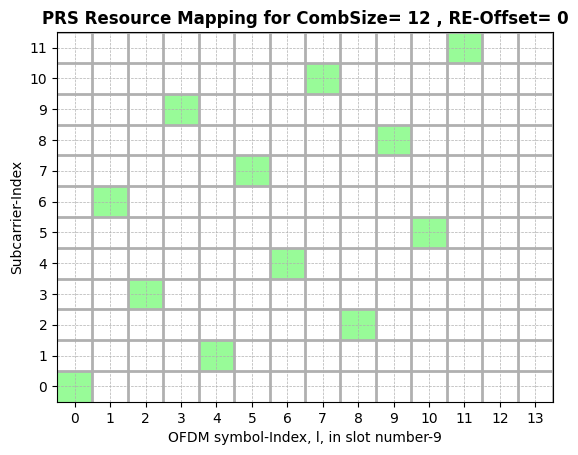
Position Reference Signal
Number of OFDM symbols occupied by PRS:
dl_PRS_NumSymbolsCOMB size-N for PRS Transmission:
dl_PRS_CombSizeNPRS symbol offset:
dl_PRS_ResourceSymbolOffsetResource Element offset in PRS:
dl_PRS_ReOffsetPRS Resource-ID:
dl_PRS_SequenceIDIndex of the Slot which will carry the PRS resource Grid:
slotNumberPower scaling factor of PRS per ofdm symbol:
betaPRSPRS Resource Grid: (prsGrid) - \(\text{N}_\text{BS} \times 14*\text{numSlots} \times 12*\text{numRBs}\)
[5]:
dl_PRS_NumSymbols = 12 # Number of OFDM symbols occupied by PRS
dl_PRS_CombSizeN = 12 #12 # COMB size-N
dl_PRS_ResourceSymbolOffset = 0 # PRS symbol offset
dl_PRS_ReOffset = 0 # RE offset in PRS # not considered
dl_PRS_SequenceID = 1031 # PRS Sequence ID.
# Number of slots per frame
numBSsPerSlot = dl_PRS_CombSizeN
numSlots = int(np.ceil(nBSs/numBSsPerSlot))
slotNumber = 9 # Index of slot where the PRS is loaded
betaPRS = 1 # power scaling factor of PRS per ofdm symbol
prsGrid = np.zeros((nBSs, 14, numRBs*12), dtype = np.complex64)
prsObject = np.empty((nBSs), dtype=object)
for nbs in range(nBSs):
slotIndex = int(nbs/numBSsPerSlot)
# Object for generating the PRS Resource Grid
prsObject[nbs] = ResourceMapperPRS(betaPRS, dl_PRS_CombSizeN, dl_PRS_ReOffset + int(nbs%numBSsPerSlot),
dl_PRS_ResourceSymbolOffset, dl_PRS_NumSymbols, dl_PRS_SequenceID+nbs)
# Generate the PRS Resource Grid
prsGrid[nbs] = prsObject[nbs](slotNumber+slotIndex, numRBs)
prsGrid = prsGrid.reshape(nBSs, -1, numRBs*12)
[6]:
f,a = prsObject[0].displayResourceGrid() # Display PRS Resource Grid
OFDM Transmitter: Create Transmission Grid
Transmission Grid:
XGridBandwidth RE Offset:
bwpOffset
[7]:
XGrid = np.zeros((nBSs, 14, Nfft), dtype = np.complex64)
bwpOffset = np.random.randint(Nfft-numRBs*12)
## Load the resource grid to Transmission Grid
XGrid[...,bwpOffset:(bwpOffset+numRBs*12)] = prsGrid
print()
print("*****************************************************")
print(" Size of the Transmission Grid: "+str(XGrid.shape))
print(" BWP Resoure Element Offset: "+str(bwpOffset))
print(" Size of the PRS-Resource Grid: "+str(prsGrid.shape))
print("*****************************************************")
print()
*****************************************************
Size of the Transmission Grid: (21, 14, 1024)
BWP Resoure Element Offset: 2
Size of the PRS-Resource Grid: (21, 14, 1020)
*****************************************************
Compute the Measurement Windows
[8]:
## Compute Measurement Window
nBeamsPhi = 64
nBeamsTheta = 1
numBeams = nBeamsPhi*nBeamsTheta
Pt_dBm = 53
Pt = 10**(0.1*(Pt_dBm-30))
lamda = 3*10**8/carrierFrequency
Nty = bsAntArray.arrayStructure[2]
Ntx = bsAntArray.arrayStructure[3]
phiMean = paramGen.phiAoD_LoS[0]*np.pi/180
phiStd = 2*np.ones((nBSs, nUEs))*np.pi/180
thetaMean = paramGen.thetaAoD_LoS[0]*np.pi/180
thetaStd = 2*np.ones((nBSs, nUEs))*np.pi/180
azimuthGrid = np.linspace(phiMean -0.5*phiStd, phiMean +0.5*phiStd, nBeamsPhi)
elevationGrid = np.linspace(thetaMean-0.5*thetaStd, thetaMean+0.5*thetaStd, nBeamsTheta)
Transmit Beamforming
Transmit Power, \(P_t\) (dBm)
Inter-Antenna spacing, d (m)
Beamformed Grid, Xf
Beamforming Direction: (0,0)
Add Noise
Noise Variance: \(k_B\) * T * B where
\(k_B\): Boltzmann Constant: \(1.380649 \times 10^{-23}\)
T: Temperature: 300 K
B: Bandwidth: 30 MHz
Carrier Frequency Offset: Not considered in this simulation
kppm (CFO in ppm of carrier frequency): 0
CFO
Received Grid with Noise (Yf)
Pass the Beamformed Grid Through Wireless Channel
OFDM Channel, Hf: (Number of Symbols (1), Number of BSs, Number of UEs, Nfft, Number of Rx Antennas, Number Tx Antennas)
Transmit Grid, Xf: (Number of BSs, Number of Tx Antennas, Number of Symbols, Nfft)
Received Grid, Y: (Number of UEs, Number of Rx Antennas, Number of Symbols, Nfft)
Note: Static Wireless Channel (No mobility is considered)
[9]:
phi = azimuthGrid[np.newaxis,:].repeat(nBeamsTheta, 0).reshape(-1, nBSs, nUEs).transpose(1,2,0)
theta = np.tile(elevationGrid[:,np.newaxis], [1, nBeamsPhi, 1, 1]).reshape(-1, nBSs, nUEs).transpose(1,2,0)
rsrp = np.zeros((nBSs, nUEs, numBeams), dtype=np.float64)
antLocations = (bsAntArray.locations[0,0,:,:,0])[np.newaxis,np.newaxis,...,:,np.newaxis]
for nue in range(nUEs):
## Transmit Beamforming
#################################################################
# Bemforming angles
# Inter-element spacing in vertical and horizontal
steeringVector = np.stack((np.sin(theta[:,nue], dtype = np.float32)*np.cos(phi[:,nue], dtype = np.float32),
np.sin(theta[:,nue], dtype = np.float32)*np.sin(phi[:,nue], dtype = np.float32),
np.cos(theta[:,nue], dtype = np.float32)), axis = -1)[...,np.newaxis,np.newaxis,np.newaxis,:]
beamVectors = (steeringVector@antLocations)[...,0,0].reshape(nBSs,numBeams,-1)/lamda
beamVectors = np.sqrt(Pt*dl_PRS_CombSizeN/Nt)*np.exp(-1j*2*np.pi*beamVectors)
Xf = np.complex64(XGrid[:,np.newaxis,...,np.newaxis]*beamVectors[...,np.newaxis,np.newaxis,:])
print(" UE-index: "+str(nue)+" | Beamforming completed!")
## Pass through the wireless Channel
Y = np.complex64((Hf[0,:,nue,np.newaxis,np.newaxis]@Xf[...,np.newaxis])[...,0])
# Add Noise
BoltzmanConst = 1.380649*(10**(-23))
temperature = 300
noisePower = BoltzmanConst*temperature*Bandwidth
kppm = 0
fCFO = kppm*(np.random.rand()-0.5)*carrierFrequency*(10**(-6)); # fCFO = CFO*subcarrierSpacing
CFO = (fCFO/scs)/Nfft
Yf = np.complex64(AddNoise(False)(Y, noisePower, 0)) #Added
# Extracting the Resource Grid
rxGrid = Yf[...,bwpOffset:(bwpOffset+numRBs*12),:].transpose(0,1,4,2,3)
# Compute the RSRP of each beam
for lbs in range(nBSs):
# print("lbs, lue",lbs, lue)
rsrp[lbs, nue] = (np.abs(rxGrid[lbs].transpose(2,3,1,0)[prsObject[lbs].prsIndices])**2).sum(0).sum(0)
print(" UE-index: "+str(nue)+" | RSRP measured!")
UE-index: 0 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 0 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 1 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 1 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 2 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 2 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 3 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 3 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 4 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 4 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 5 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 5 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 6 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 6 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 7 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 7 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 8 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 8 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 9 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 9 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 10 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 10 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 11 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 11 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 12 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 12 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 13 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 13 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 14 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 14 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 15 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 15 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 16 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 16 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 17 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 17 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 18 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 18 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 19 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 19 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 20 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 20 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 21 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 21 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 22 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 22 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 23 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 23 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 24 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 24 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 25 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 25 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 26 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 26 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 27 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 27 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 28 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 28 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 29 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 29 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 30 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 30 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 31 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 31 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 32 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 32 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 33 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 33 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 34 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 34 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 35 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 35 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 36 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 36 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 37 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 37 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 38 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 38 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 39 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 39 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 40 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 40 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 41 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 41 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 42 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 42 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 43 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 43 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 44 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 44 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 45 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 45 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 46 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 46 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 47 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 47 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 48 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 48 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 49 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 49 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 50 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 50 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 51 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 51 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 52 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 52 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 53 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 53 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 54 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 54 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 55 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 55 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 56 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 56 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 57 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 57 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 58 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 58 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 59 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 59 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 60 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 60 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 61 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 61 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 62 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 62 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 63 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 63 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 64 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 64 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 65 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 65 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 66 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 66 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 67 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 67 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 68 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 68 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 69 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 69 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 70 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 70 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 71 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 71 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 72 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 72 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 73 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 73 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 74 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 74 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 75 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 75 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 76 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 76 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 77 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 77 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 78 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 78 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 79 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 79 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 80 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 80 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 81 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 81 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 82 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 82 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 83 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 83 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 84 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 84 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 85 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 85 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 86 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 86 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 87 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 87 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 88 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 88 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 89 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 89 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 90 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 90 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 91 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 91 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 92 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 92 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 93 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 93 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 94 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 94 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 95 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 95 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 96 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 96 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 97 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 97 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 98 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 98 | RSRP measured!
UE-index: 99 | Beamforming completed!
UE-index: 99 | RSRP measured!
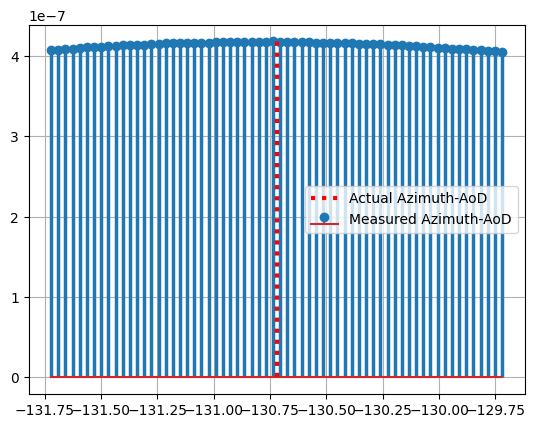
RSRP vs beam Index
[10]:
ueIndex = 0
bsIndex = 0
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
# markerline, stemlines, baseline = ax.stem(azimuthGridNew, rsrpNew, 'g', label = "Interpolated Azimuth-AoD")
# stemlines.set_linewidth(1)
# markerline.set_markersize(2)
# stemlines.set_linestyles(":")
markerline, stemlines, baseline = ax.stem(azimuthGrid[:,bsIndex,ueIndex]*180/np.pi, rsrp[bsIndex,ueIndex].reshape(nBeamsTheta, nBeamsPhi).sum(0), label = "Measured Azimuth-AoD")
stemlines.set_linewidth(2.5)
markerline.set_markersize(6)
ax.vlines(paramGen.phiAoD_LoS[0,bsIndex,ueIndex], ymin = 0, ymax = rsrp[bsIndex,ueIndex].reshape(nBeamsTheta, nBeamsPhi).sum(0).max(), color = "r", lw = 3, ls = ":", label = "Actual Azimuth-AoD")
ax.legend(loc = 'best')
ax.grid()
plt.show()
AoD Estimation
[11]:
xoAEst = np.zeros((nBSs, nUEs, 2))
xoA = np.stack((paramGen.phiAoD_LoS[0], paramGen.thetaAoD_LoS[0]), axis = -1)*np.pi/180
beamIndices = rsrp.argmax(-1)
for nbs in range(nBSs):
for nue in range(nUEs):
xoAEst[nbs,nue, 0] = phi[nbs,nue, beamIndices[nbs,nue]]
xoAEst[nbs,nue, 1] = theta[nbs,nue, beamIndices[nbs,nue]]
Position Estimation + K-Best Measurement Selection (Genie Aided)
Measurement Selection:
Select the most accurate k ToA measnurements for Positioning
Even 1 Inaccuracte measurement can compromise the positioning performance.
Genie Aided Measurement Selection: Assumes that the accuracy of the each measurment is known somehow.
Selects the best ToA-measurements available to each UE from the BSs for estimating the location.
[12]:
rxPosition = simLayoutObj.UELocations
txPosition = simLayoutObj.BSLocations
k = 4 # Select k-best measurements
error = np.abs(xoAEst[...,0] - xoA[...,0]) # Compute the ToA error in each measurement
# Position Estimation Object:
# Positioning based on: DoA
# Optimization Method: Gradient Descent
posEstimator = LeastSquareDoA()
rxPositionEstimate = np.zeros((nUEs, 3))
std = np.zeros((nUEs, 2))
kBestIndices = np.zeros((nUEs, k), dtype = np.int8)
for nue in range(nUEs):
bsIndices = np.argmin(error[..., nue].reshape(-1, 3), axis = -1)
siteIndices = np.argsort(np.min(error[..., nue].reshape(-1, 3), -1))[0:k]
kBestIndices[nue] = siteIndices*nSectorsPerSite + bsIndices[siteIndices]
rxPositionEstimate[nue], std[nue] = posEstimator(txPosition[kBestIndices[nue]], xoAEst[kBestIndices[nue],nue])
print("nue: "+str(nue)+" | Rx Location Estimate: "+str(rxPositionEstimate[nue]))
nue: 0 | Rx Location Estimate: [-359.01876144 -417.47088924 29.41016588]
nue: 1 | Rx Location Estimate: [ 42.78669819 174.58115965 30.51680364]
nue: 2 | Rx Location Estimate: [ 779.10774189 -174.81345912 28.66695834]
nue: 3 | Rx Location Estimate: [ 182.05063066 -279.76018999 24.4014134 ]
nue: 4 | Rx Location Estimate: [-43.97485771 725.42467735 28.03582379]
nue: 5 | Rx Location Estimate: [418.68949763 4.63860667 29.95735549]
nue: 6 | Rx Location Estimate: [-347.31445659 -203.84958682 33.62075529]
nue: 7 | Rx Location Estimate: [-395.13081408 106.3275688 26.66068703]
nue: 8 | Rx Location Estimate: [ 305.60487736 -776.44800372 27.75456728]
nue: 9 | Rx Location Estimate: [-576.9003876 49.71920292 28.06830207]
nue: 10 | Rx Location Estimate: [-334.75067944 -262.58239455 30.19317779]
nue: 11 | Rx Location Estimate: [ 46.18868112 312.28143355 30.66991935]
nue: 12 | Rx Location Estimate: [679.37966381 481.38075781 29.23397206]
nue: 13 | Rx Location Estimate: [-318.50683548 545.15121481 34.32300754]
nue: 14 | Rx Location Estimate: [-559.30578699 -215.5184474 29.09216752]
nue: 15 | Rx Location Estimate: [2368.5875262 635.42440274 41.81445601]
nue: 16 | Rx Location Estimate: [1906.8665596 -791.68524732 39.46693427]
nue: 17 | Rx Location Estimate: [2590.51569143 431.75573784 43.31983926]
nue: 18 | Rx Location Estimate: [1456.77187222 231.12215914 46.07774653]
nue: 19 | Rx Location Estimate: [2382.16254384 104.21674582 39.19592682]
nue: 20 | Rx Location Estimate: [1387.33095929 -543.99864225 35.32340611]
nue: 21 | Rx Location Estimate: [2055.50388465 694.28497084 46.3900648 ]
nue: 22 | Rx Location Estimate: [1158.26048815 414.02959409 32.72228914]
nue: 23 | Rx Location Estimate: [1349.81287085 -12.93856921 44.17215767]
nue: 24 | Rx Location Estimate: [2052.24832918 741.11608934 46.39182262]
nue: 25 | Rx Location Estimate: [1647.43827205 -602.81414949 38.44005139]
nue: 26 | Rx Location Estimate: [2471.5986077 -13.3680525 48.59277088]
nue: 27 | Rx Location Estimate: [1327.23205468 -134.94130645 33.83156608]
nue: 28 | Rx Location Estimate: [2236.41048839 559.15011382 45.85800926]
nue: 29 | Rx Location Estimate: [1410.0594 437.43269124 35.12643322]
nue: 30 | Rx Location Estimate: [1663.09387474 1634.92986144 43.85570637]
nue: 31 | Rx Location Estimate: [ 86.75362162 1409.41515279 31.92185182]
nue: 32 | Rx Location Estimate: [ 67.70080146 1651.31026302 30.07257801]
nue: 33 | Rx Location Estimate: [486.97779167 776.71374113 28.86127804]
nue: 34 | Rx Location Estimate: [ 13.19397683 1350.02714357 30.45520646]
nue: 35 | Rx Location Estimate: [1402.61079238 1559.69378179 38.22889458]
nue: 36 | Rx Location Estimate: [ 813.04515911 1935.29235127 49.92112269]
nue: 37 | Rx Location Estimate: [1486.22465188 1009.23907728 42.53187137]
nue: 38 | Rx Location Estimate: [ 88.36130781 1110.40170535 27.75877958]
nue: 39 | Rx Location Estimate: [1262.66757708 2198.21464019 48.35152197]
nue: 40 | Rx Location Estimate: [1221.4887303 1288.78872932 35.44011282]
nue: 41 | Rx Location Estimate: [ 59.19047402 1394.60711561 31.07534023]
nue: 42 | Rx Location Estimate: [542.46449497 984.70649096 36.42142474]
nue: 43 | Rx Location Estimate: [ 790.239718 1301.40456874 41.99330555]
nue: 44 | Rx Location Estimate: [-860.14610741 1735.78429058 39.64408335]
nue: 45 | Rx Location Estimate: [-969.48684934 2404.42615328 44.58621319]
nue: 46 | Rx Location Estimate: [-1134.82147955 2294.01818634 48.45202281]
nue: 47 | Rx Location Estimate: [-342.9157313 1679.30515952 32.57225551]
nue: 48 | Rx Location Estimate: [-730.84942838 736.3472413 36.94300512]
nue: 49 | Rx Location Estimate: [-816.78895508 1609.24331023 37.97490925]
nue: 50 | Rx Location Estimate: [-177.88119986 1149.67488905 30.53432483]
nue: 51 | Rx Location Estimate: [-547.69956874 1873.02627622 45.21545543]
nue: 52 | Rx Location Estimate: [-352.33454538 2009.3689197 46.74280221]
nue: 53 | Rx Location Estimate: [-1730.56175809 1290.26476032 42.26835123]
nue: 54 | Rx Location Estimate: [-283.45938857 935.10717211 29.90767655]
nue: 55 | Rx Location Estimate: [-1229.1693352 1399.97775435 42.17238544]
nue: 56 | Rx Location Estimate: [-1102.92491167 1531.1702206 33.49089528]
nue: 57 | Rx Location Estimate: [-693.17734376 730.29430399 30.07834947]
nue: 58 | Rx Location Estimate: [-1982.29472944 -18.97878568 48.65760135]
nue: 59 | Rx Location Estimate: [-2142.39537827 647.3928471 45.40096387]
nue: 60 | Rx Location Estimate: [-2412.80617459 -18.58952957 48.7406165 ]
nue: 61 | Rx Location Estimate: [-2063.61114326 627.06836296 47.50960189]
nue: 62 | Rx Location Estimate: [-2251.37727569 294.62929819 51.42629727]
nue: 63 | Rx Location Estimate: [-2406.30027313 -389.6391116 57.37741679]
nue: 64 | Rx Location Estimate: [-2376.10349713 616.55458813 52.633375 ]
nue: 65 | Rx Location Estimate: [-1881.49272956 -168.95006205 46.8512651 ]
nue: 66 | Rx Location Estimate: [-1616.3788927 587.57797906 40.53307558]
nue: 67 | Rx Location Estimate: [-2246.83339547 -672.96263995 41.05195825]
nue: 68 | Rx Location Estimate: [-1493.37269841 347.65312303 39.51736564]
nue: 69 | Rx Location Estimate: [-2333.13188826 -400.99405237 48.98471568]
nue: 70 | Rx Location Estimate: [-1893.04890434 280.7433992 45.83153548]
nue: 71 | Rx Location Estimate: [-1711.31276025 917.93176809 44.24532617]
nue: 72 | Rx Location Estimate: [ -684.50866104 -1814.1033381 39.20054161]
nue: 73 | Rx Location Estimate: [ -667.31562928 -2273.74722883 52.150375 ]
nue: 74 | Rx Location Estimate: [-1144.31590136 -2016.75718266 32.42903418]
nue: 75 | Rx Location Estimate: [-569.4109725 -883.99722987 30.03101273]
nue: 76 | Rx Location Estimate: [-1076.19568404 -2114.78498633 54.00410155]
nue: 77 | Rx Location Estimate: [ -461.4559225 -1333.63924489 30.11010613]
nue: 78 | Rx Location Estimate: [-1695.36953111 -1813.65305988 55.45221372]
nue: 79 | Rx Location Estimate: [ -695.08475296 -1744.0502098 45.9867078 ]
nue: 80 | Rx Location Estimate: [-1197.41226215 -755.22717687 37.93978465]
nue: 81 | Rx Location Estimate: [ -76.23904268 -1415.12273306 28.62348287]
nue: 82 | Rx Location Estimate: [ -186.27005466 -1615.65180073 32.31867804]
nue: 83 | Rx Location Estimate: [ -799.31871766 -1725.4556035 46.29838114]
nue: 84 | Rx Location Estimate: [ -588.67700583 -1637.65770434 36.57990531]
nue: 85 | Rx Location Estimate: [-1505.83197435 -1375.59758004 54.85237886]
nue: 86 | Rx Location Estimate: [ 1201.76762636 -1122.7141471 44.37681137]
nue: 87 | Rx Location Estimate: [ 1281.41068836 -1652.65774792 51.63387359]
nue: 88 | Rx Location Estimate: [ 762.21947203 -999.14308765 32.21407282]
nue: 89 | Rx Location Estimate: [ 253.13034854 -2074.25781085 34.30823231]
nue: 90 | Rx Location Estimate: [ 1377.79550784 -1810.07727844 47.19178143]
nue: 91 | Rx Location Estimate: [ 469.66045386 -1280.53616327 44.24595016]
nue: 92 | Rx Location Estimate: [ 1272.20853414 -1058.99189859 34.7584014 ]
nue: 93 | Rx Location Estimate: [ 1418.51259671 -2154.39879911 51.08808944]
nue: 94 | Rx Location Estimate: [ 1307.051491 -1184.32848574 40.85571692]
nue: 95 | Rx Location Estimate: [ 998.14092356 -1608.59937354 39.46111491]
nue: 96 | Rx Location Estimate: [ 1244.89130973 -1911.9021219 46.96026782]
nue: 97 | Rx Location Estimate: [ 1332.68917835 -1022.5080149 35.65556915]
nue: 98 | Rx Location Estimate: [ 198.32076588 -1645.18490969 34.31428473]
nue: 99 | Rx Location Estimate: [ 239.27480029 -1127.49411185 24.71727841]
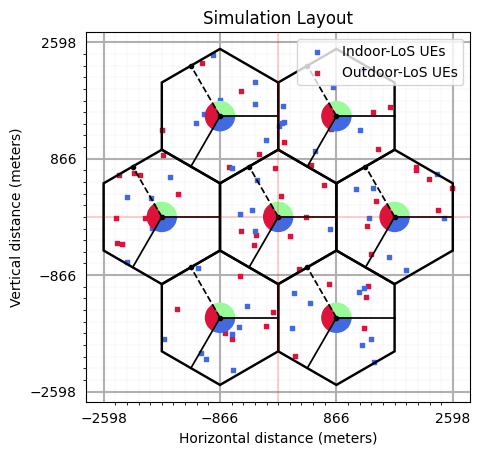
Visualization of Positioning
Show the accurcy of positioning by comparing the actual location against the true location.
Note: Please use the intractive matplotlib %matplotlib widget to see this graph.
[13]:
## PSS Detection Plot
#################################################################
rxPosition = simLayoutObj.UELocations
txPosition = simLayoutObj.BSLocations
# rangeEst_2D = np.sqrt(np.abs((ToAe*(3*10**8))**2 - (rxPosition[:,2].reshape(1,-1)-txPosition[:,2].reshape(-1,1))**2))
# fig, ax = plt.subplots()
fig, ax = simLayoutObj.display2DTopology(isEqualAspectRatio = True)
colors = ["k","m","r","b","g","y","crimson"]
linestyle_tuple = ['solid', 'dotted', 'dashed', 'dashdot',
(0, (5, 10)), # 'loosely dashed'
(0, (1, 10)), # 'loosely dotted'
(5, (10, 3)), # 'long dash with offset'
(0, (5, 1)), # 'densely dashed'
(0, (3, 10, 1, 10)), # 'loosely dashdotted'
(0, (3, 5, 1, 5)), # 'dashdotted'
(0, (3, 1, 1, 1)), # 'densely dashdotted'
(0, (3, 5, 1, 5, 1, 5)), # 'dashdotdotted'
(0, (3, 10, 1, 10, 1, 10)), # 'loosely dashdotdotted'
(0, (3, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1))] # 'densely dashdotdotted'
# for nbs in range(k):
# for nue in range(nUEs):
# circle1 = plt.Circle((txPosition[kBestIndices[nue, nbs], 0], txPosition[kBestIndices[nue, nbs], 1]), rangeEst_2D[kBestIndices[nue, nbs], nue],
# color = colors[nue%7], lw = 0.35, ls = linestyle_tuple[nue%7], fill = False, zorder = 0)
# ax.add_artist(circle1)
ax.scatter(txPosition[:,0], txPosition[:,1], marker="P", color="b", edgecolors='white',
s = 125, label="Tx-Locations", zorder = 3)
ax.scatter(rxPositionEstimate[:,0], rxPositionEstimate[:,1], marker="o", color="g",
s = 75, label="Estimated Rx-Locations", zorder = 1)
ax.scatter(rxPosition[:,0], rxPosition[:,1], marker=".", color="r", edgecolors='white',
s = 100, label="True Rx-Locations", zorder = 2)
ax.legend()
ax.set_title("Transmitter's Locations and Estimation Accuracy (True UE Location vs Estimated UE Locations)")
# ax.set_xlim([-200, 200])
# ax.set_ylim([-200, 200])
ax.grid(True)
Performance Analysis of Positioning Error for ToA based method
The perfrormance of the positioning methods is analyzed using:
50 percentile Position Error in Horizontal and Vertical Direction.
67 percentile Position Error in Horizontal and Vertical Direction.
90 percentile Position Error in Horizontal and Vertical Direction.
Fraction of users which are positioned with accuracy better ththan 50 cm.
[14]:
nbins = nUEs
xlimit = 2.5
ylimit = 1
posError3D = np.linalg.norm(rxPositionEstimate-rxPosition[:], axis=1)
posError3D = np.where(np.isnan(posError3D), 0, posError3D)
posError2D = np.linalg.norm(rxPositionEstimate[:, 0:2]-rxPosition[:, 0:2], axis=1)
# Horizontal Error
count, bins_count = np.histogram(posError2D, bins = nbins, range = [0, xlimit])
pdf = count/nUEs
cdf = np.cumsum(pdf)
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot(bins_count[1:], cdf, label = "2D Positioning Error")
# Vertical Error
count, bins_count = np.histogram(posError3D, bins = nbins, range = [0, xlimit])
pdf = count/nUEs
cdf = np.cumsum(pdf)
ax.plot(bins_count[1:], cdf, label = "Vertical Positioning Error")
ax.set_xticks(np.linspace(0, xlimit, 11))
ax.set_xticks(np.linspace(0, xlimit, 21), minor=True)
ax.set_yticks(np.linspace(0, ylimit, 11))
ax.set_yticks(np.linspace(0, ylimit, 21), minor=True)
ax.set_xlabel("Positioning Error (m)")
ax.set_ylabel("CDF of Positioning Error")
ax.set_title("CDF of Positioning Error")
ax.axhline(y = 0.2, lw = 2, alpha = 1, linestyle = ':', color = "crimson", label = "50%ile Positioning Error line")
ax.axhline(y = 2/3, lw = 2, alpha = 1, linestyle = ':', color = "magenta", label = "66.6%ile Positioning Error line")
ax.axhline(y = 0.9, lw = 2, alpha = 1, linestyle = ':', color = "royalblue", label = "90%ile Positioning Error line")
ax.axvline(x = 1.5, lw = 2, alpha = 1, linestyle = '-', color = "midnightblue", label = "50 cm Positioning Accuracy line")
# Specify different settings for major and minor grids
ax.grid(which = 'minor', alpha = 0.25, linestyle = '--')
ax.grid(which = 'major', alpha = 1)
ax.set_xlim([0,xlimit])
ax.set_ylim([0,ylimit])
ax.legend()
plt.show()
# # Code to save the Database
# idx = 0
# flag = True
# while(flag):
# print("flag: "+str(idx)+" | i="+str(idx))
# filename = "Databases/DLAoD-"+str([idx])+".npz"
# if(os.path.exists(filename)):
# idx = idx + 1
# else:
# np.savez(filename, posError3D = posError3D, posError2D = posError2D,
# rxPositionEstimate = rxPositionEstimate, rxPosition = rxPosition,
# xoA = xoA, xoAEst = xoAEst, txPosition = txPosition, scs = scs,
# carrierFrequency = carrierFrequency, Nfft = Nfft, nBSs = nBSs,
# nUEs = nUEs, numRBs = numRBs, propTerrain = propTerrain,
# bsArrayStructure = bsAntArray.arrayStructure,
# ueArrayStructure = ueAntArray.arrayStructure)
# flag = False
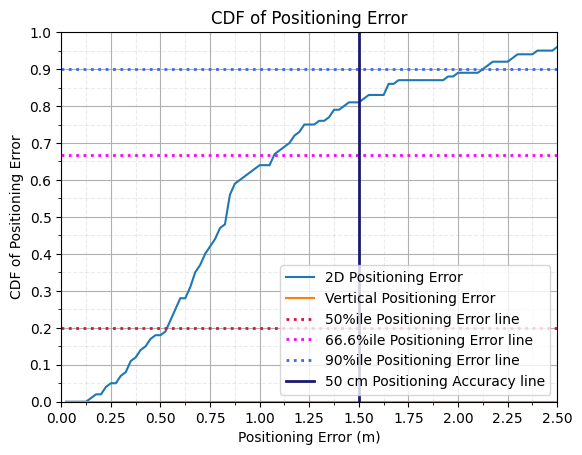
Performance Analysis for DL-AoD method: 2000 UEs
[17]:
filename = "Databases/DLAoD-"+str([0])+".npz"
ds = np.load(filename)
posError3D = ds["posError3D"]
posError2D = ds["posError2D"]
for i in range(1,9):
filename = "Databases/DLAoD-"+str([i])+".npz"
ds = np.load(filename)
posError3D = np.concatenate([posError3D, ds["posError3D"]])
posError2D = np.concatenate([posError2D, ds["posError2D"]])
nbins = int(posError2D.size)
xlimit = 2.5
ylimit = 1
# Horizontal Error
count, bins_count = np.histogram(posError2D, bins = nbins, range = [0, xlimit])
pdf = count/count.sum()
cdf = np.cumsum(pdf)
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot(bins_count[1:], cdf, label = "2D Positioning Error")
# Vertical Error
count, bins_count = np.histogram(posError3D, bins = nbins, range = [0, xlimit])
pdf = count/count.sum()
cdf = np.cumsum(pdf)
ax.plot(bins_count[1:], cdf, label = "Vertical Positioning Error")
ax.set_xticks(np.linspace(0, xlimit, 11))
ax.set_xticks(np.linspace(0, xlimit, 21), minor=True)
ax.set_yticks(np.linspace(0, ylimit, 11))
ax.set_yticks(np.linspace(0, ylimit, 21), minor=True)
ax.set_xlabel("Positioning Error (m)")
ax.set_ylabel("CDF of Positioning Error")
ax.set_title("CDF of Positioning Error")
ax.axhline(y = 0.2, lw = 2, alpha = 1, linestyle = ':', color = "crimson", label = "50%ile Positioning Error line")
ax.axhline(y = 2/3, lw = 2, alpha = 1, linestyle = ':', color = "magenta", label = "66.6%ile Positioning Error line")
ax.axhline(y = 0.9, lw = 2, alpha = 1, linestyle = ':', color = "royalblue", label = "90%ile Positioning Error line")
ax.axvline(x = 1.6,lw = 2, alpha = 1, linestyle = '-', color = "midnightblue", label = "50 cm Positioning Accuracy line")
# Specify different settings for major and minor grids
ax.grid(which = 'minor', alpha = 0.25, linestyle = '--')
ax.grid(which = 'major', alpha = 1)
ax.set_xlim([0,xlimit])
ax.set_ylim([0,ylimit])
ax.legend()
plt.show()
/tmp/ipykernel_56393/3860440226.py:29: RuntimeWarning: invalid value encountered in divide
pdf = count/count.sum()
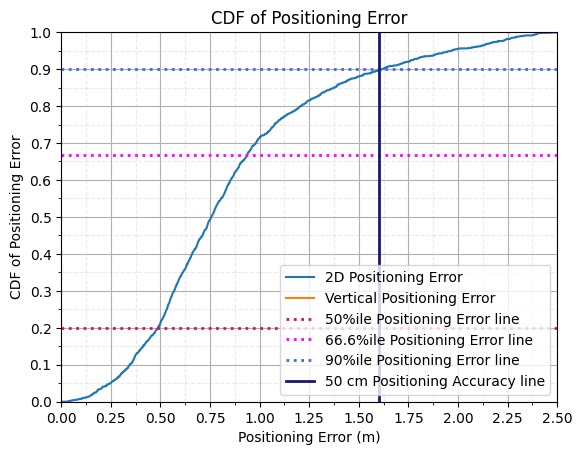
Further Study
The tutorial can be extended further to study the effect of:
Subcarrier Spacing (\(\Delta f\))
Carrier Frequency (\(f_c\))
Bandwidth (\(B\))
NLoS Probability (\(p_{LOS}\))
Transmitter Power (\(P_t\))
Number of Base-stations (\(N_{BS}\))
Comb-factor (\(K_{comb}\))
on positioning accuracy. Furthermore, different terrians have different propagation characteristics. These characteristics effect the accuracy of positioning.
Thanks for reading the tutorial!
[ ]: