8. Blind Decoding Of Physical Downlink Control Channel on Plutto-SDR
The tutorial demonstrates the downlink synchronization using synchronization signal block (SSB) and PDCCH blind decoding in 5G networks. The SSB consists of 4 elements:
Primary Synchronization Signal (PSS)
Secondary Synchronization Signal (SSS)
Physical Broadacast Channel (PBCH) Payload: 432 symbols
Demodulation Reference Signal (DMRS) for PBCH
The PDCCH consists of 2 elements: - Define the PDCCH coreset and search space set parameters. - Aggregation level - frequency domain resources - duration - monitoring symbols with in a slot - search space set type - CCE to REG mapping - REG bundle size - Interleaver size - shift index
Decode the PDCCH candidates blindly based on the chosen parameters.
The tutorial performs following procedures:
-
Generate PSS
Generate PSS
Generate PBCH
Generate DMRS-PBCH
Generate SSB
-
Insert SSB to Tx Resource Grid
OFDM Modulation
-
Channel Estimation
Equalization
-
MIB Decoding
ATI Decoding
8. Import Libraries
8. Import Python and SDR Libraries
[1]:
# %matplotlib widget
# from IPython.display import display, HTML
# display(HTML("<style>.container { width:90% !important; }</style>"))
import os
os.environ["CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES"] = "-1"
os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '3'
import matplotlib as mpl
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.patches as patches
import matplotlib.animation as animation
import numpy as np
import adi
8. Import 5G Toolkit Libraries
[2]:
import sys
sys.path.append(".")
from toolkit5G.SequenceGeneration import PSS, SSS, DMRS
from toolkit5G.PhysicalChannels import PBCH, PBCHDecoder, PDCCH, PDCCHDecoder, PDCCHCandidateBlindDecoding
from toolkit5G.ResourceMapping import SSB_Grid, ResourceMapperSSB, ResourceMappingPDCCH, CORESET, SearchSpaceSet
from toolkit5G.OFDM import OFDMModulator, OFDMDemodulator
from toolkit5G.MIMOProcessing import AnalogBeamforming, ReceiveCombining
from toolkit5G.ReceiverAlgorithms import PSSDetection, SSSDetection, ChannelEstimationAndEqualization, DMRSParameterDetection
from toolkit5G.ReceiverAlgorithms import ChannelEstimationAndEqualizationPBCH, ChannelEstimationAndEqualizationPDCCH
from toolkit5G.Configurations import TimeFrequency5GParameters, GenerateValidSSBParameters
8. Emulation Configurations
[3]:
###################
# System Parameters
###################
center_frequency = 2*1e9 # center or carrier frequency in Hz
numerology = 0
slotNumber = 0
# OFDM Parameters
Bandwidth = 30*10**6
fftSize = 2048
subcarrier_spacing = 15000
numOFDMSymbols = 14
sample_rate = fftSize*subcarrier_spacing
# Pulse Shaping
numSamplesPerSymbol = 1
# number of samples returned per call to rx()
buffer_size = int(fftSize*1.2*numSamplesPerSymbol*numOFDMSymbols)
8. Transmitter Implementation
8. Generate the SSB Grid for synchronization
[4]:
## This class fetches valid set of 5G parameters for the system configurations
nSymbolFrame= int(140*subcarrier_spacing/15000)
## This class fetches valid set of 5G parameters for the system configurations
tfParams = TimeFrequency5GParameters(Bandwidth, subcarrier_spacing)
tfParams(nSymbolFrame, typeCP = "normal")
nRB = tfParams.numRBs # SSB Grid size (Number of RBs considered for SSB transition)
Neff = tfParams.Neff # Number of resource blocks for Resource Grid ( exclude gaurd band | offsets : BWP)
Nfft = 512 # FFT-size for OFDM
lengthCP = tfParams.lengthCP # CP length
#___________________________________________________________________
#### Generate MIB Information
lamda = 3e8/center_frequency;
nSCSOffset = 1
ssbParameters = GenerateValidSSBParameters(center_frequency, nSCSOffset, "caseA")
systemFrameNumber = ssbParameters.systemFrameNumber
subCarrierSpacingCommon = subcarrier_spacing
ssbSubCarrierOffset = ssbParameters.ssbSubCarrierOffset
DMRSTypeAPosition = ssbParameters.DMRSTypeAPosition
controlResourceSet0 = ssbParameters.controlResourceSet0
searchSpace0 = ssbParameters.searchSpace0
isPairedBand = ssbParameters.isPairedBand
nSCSOffset = ssbParameters.nSCSOffset
choiceBit = ssbParameters.choiceBit
ssbType = ssbParameters.ssbType
nssbCandidatesInHrf = ssbParameters.nssbCandidatesInHrf
ssbIndex = ssbParameters.ssbIndex
hrfBit = ssbParameters.hrfBit
cellBarred = ssbParameters.cellBarred
intraFrequencyReselection = ssbParameters.intraFrequencyReselection
withSharedSpectrumChannelAccess = ssbParameters.withSharedSpectrumChannelAccess
Nsc_ssb = 240
Nsymb_ssb = 4
#_______________________________________
N_ID2 = np.random.randint(3)
# Generate PSS sequence
pssObject = PSS(N_ID2);
pssSequence = pssObject()
N_ID1 = np.random.randint(336)
N_ID = 3*N_ID1 + N_ID2
# Generate SSS sequence
sssObject = SSS(N_ID1, N_ID2);
sssSequence = sssObject()
# Generate DMRS sequence
dmrsLen = 144;
dmrsObject = DMRS("PBCH", N_ID, ssbIndex, nssbCandidatesInHrf, hrfBit)
# dmrsSeq = dmrs.getSequence("tensorflow")
dmrsSequence = dmrsObject(dmrsLen)
# Generate PBCH symbols
pbchObject = PBCH(center_frequency, choiceBit, subCarrierSpacingCommon, DMRSTypeAPosition,
controlResourceSet0, searchSpace0, cellBarred, intraFrequencyReselection,
systemFrameNumber, ssbSubCarrierOffset, hrfBit, ssbIndex, N_ID,
nssbCandidatesInHrf)
pbchSymbols = pbchObject()
## Generate SSB Object
ssbObject = SSB_Grid(N_ID, True)
ssb = ssbObject(pssSequence, sssSequence, dmrsSequence, pbchSymbols)
## Loading SSB to Resource Grid
#####################################
# ssbPositionInBurst = np.ones(nssbCandidatesInHrf, dtype=int)
ssbPositionInBurst = np.zeros(nssbCandidatesInHrf, dtype=int)
ssbPositionInBurst[0] = 1
ssbRGobject = ResourceMapperSSB(ssbType=ssbType, carrierFrequency = center_frequency,
isPairedBand = isPairedBand,
withSharedSpectrumChannelAccess = withSharedSpectrumChannelAccess)
ssbGrid = ssbRGobject(ssb[0], ssbPositionInBurst, offsetInSubcarriers = ssbSubCarrierOffset[0],
offsetInRBs = 0, numRBs = nRB)[0:14]
fig, ax = ssbObject.displayGrid(option=1)
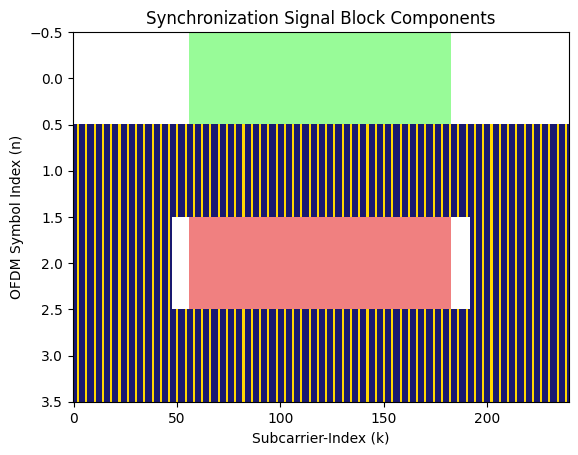
[5]:
ssbGrid.shape
[5]:
(14, 1920)
8. CORESET and Search Space Set Parameters
[6]:
AggLevel = 2
monitoringSymbolsWithinSlot = np.array([1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0], dtype = int)
startSymIndex = np.nonzero(monitoringSymbolsWithinSlot)[0][0]
coresetID = 1
cce_reg_Mapping = "interleaved" # CCE to REG mapping type
L = 6 # REG-bundle size
R = 2 # Interleaver size
nshift = 0 # cyclic-shift index after interleaving
duration = 1 # duration of CORESET
frequencyDomainResources = np.array([1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,0,
0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,
0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,
0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,
0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0], dtype = int)
RNTI = int(1 + np.random.randint(65518, dtype = int)) # radio network temporary indentifier
coresetObj = CORESET(duration,frequencyDomainResources)
coresetPRBIndices = coresetObj(cce_REG_MappingType = cce_reg_Mapping,
reg_BundleSize=L, interleaverSize = R, shiftIndex = nshift)
ssType = "USS"
AggLevel = 2 # Aggregation level
coresetSize = coresetObj.numCCESInCoreset # CORESET size in number of CCEs
numCandidatesPerAL = np.array([2,4,0,0,0], dtype=int) # number of pdcch candidates per Aggregation Level.
ssObj = SearchSpaceSet(numerology = numerology, searchSpaceType = ssType,
numCandidates = numCandidatesPerAL, coresetDuration = duration)
##############
# CCE indices
##############
M = numCandidatesPerAL[int(np.log2(AggLevel))]
ueCand = ssObj(AggLevel,RNTI,coresetSize,slotNumber,coresetID)
ueCCEs = ueCand[np.random.randint(M)]
print("#####################################################################")
print("Duration of CORESET:", duration)
print()
print("Frequency Domain Resources:", frequencyDomainResources)
print()
print("CORESET size in CCEs:", coresetObj.numCCESInCoreset)
print()
print("Monitoring Symbols With in a Slot:", monitoringSymbolsWithinSlot)
print()
print("CORESET Start symbol index:", startSymIndex)
print()
print("#####################################################################")
print("Candidates Corresponding to UE with a chosen Aggregation Level of " + str(AggLevel) + ":\n", ueCand)
print()
print("CCEs chosen for UE:\n", ueCCEs)
#####################################################################
Duration of CORESET: 1
Frequency Domain Resources: [1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0]
CORESET size in CCEs: 8
Monitoring Symbols With in a Slot: [1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0]
CORESET Start symbol index: 0
#####################################################################
Candidates Corresponding to UE with a chosen Aggregation Level of 2:
[[0 1]
[2 3]
[4 5]
[6 7]]
CCEs chosen for UE:
[0 1]
C:\Users\asnat\Downloads\May4\May4\toolkit5G\ResourceMapping\searchspaceset.py:506: RuntimeWarning: overflow encountered in long_scalars
Y[p][nsf_mu] = (A[p]*Y[p][nsf_mu - 1])%D
[7]:
nBatches = 1 # number of batches
numPDCCHSym = int(54*AggLevel) # number of REs occupied by PDCCH data (QPSK symbols)
numPDCCHdmrs = int(18*AggLevel) # number of REs occupied by PDCCH DMRS symbols
E = numPDCCHSym*2 # number of target Bits
K = 20 # payload size in bits
dciBits = np.random.randint(0, 2, [nBatches, K])
##############################################
# PDCCH chain and generation of QPSK symbols
##############################################
pdcchObj = PDCCH(K, E, RNTI, N_ID)
symb = pdcchObj(dciBits)
###################
# Resource Mappping
###################
rmPDCCH = ResourceMappingPDCCH(numerology, frequencyDomainResources, duration, monitoringSymbolsWithinSlot)
pdcchGrid = rmPDCCH(symb, cce_reg_Mapping, L, R, nshift, slotNumber, N_ID, ueCCEs)
[8]:
pdcchGrid.shape
[8]:
(1, 14, 3240)
8. Display Grids
8. PDCCH Grid
[9]:
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
colors = ['palegreen', 'white', 'lightcoral', 'gold', 'midnightblue', 'purple']
# Grid = pdcchGrid[0][...,0:ssbGrid.shape[-1]]
Grid = pdcchGrid[0]
plt.imshow(np.abs(Grid).T, interpolation='none', aspect = "auto", cmap="hot", origin='lower')
ax.tick_params(axis='both',which='minor', grid_linewidth= 2, width=0)
ax.tick_params(axis='both',which='major', grid_linewidth=0.5, grid_linestyle = '--')
ax.grid(which='both')
ax.set_xlabel("Subcarrier-Index (k)")
ax.set_ylabel("OFDM Symbol Index (n)")
plt.show()
8. SSB Grid
[10]:
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
colors = ['palegreen', 'white', 'lightcoral', 'gold', 'midnightblue', 'purple']
bounds = [0,1,2,3,4,5,6]
plt.imshow(np.abs(ssbGrid.T), interpolation='none', aspect = "auto", cmap="hot", origin='lower')
ax.tick_params(axis='both',which='minor', grid_linewidth= 2, width=0)
ax.tick_params(axis='both',which='major', grid_linewidth=0.5, grid_linestyle = '--')
ax.grid(which='both')
ax.set_ylabel("Subcarrier-Index (k)")
ax.set_xlabel("OFDM Symbol Index (n)")
plt.show()
8. SSB, PDCCH Merged Grid
[11]:
resourceGrid = ssbGrid
resourceGrid = resourceGrid + np.sqrt(1/127)*pdcchGrid[0,:,0:Neff] # make sure that the merged grids of SSB and PDCCH do not overlap.
[12]:
resourceGrid.shape
[12]:
(14, 1920)
[13]:
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
colors = ['white', 'palegreen', 'lightcoral', 'gold', 'midnightblue', 'purple']
bounds = [0,1,2,3,4,5,6]
plt.imshow(np.abs(resourceGrid.T), interpolation='none', aspect = "auto", cmap="hot", origin='lower')
ax.tick_params(axis='both',which='minor', grid_linewidth= 2, width=0)
ax.tick_params(axis='both',which='major', grid_linewidth=0.5, grid_linestyle = '--')
ax.grid(which='both')
ax.set_ylabel("Subcarrier-Index (k)")
ax.set_xlabel("OFDM Symbol Index (n)")
plt.show()
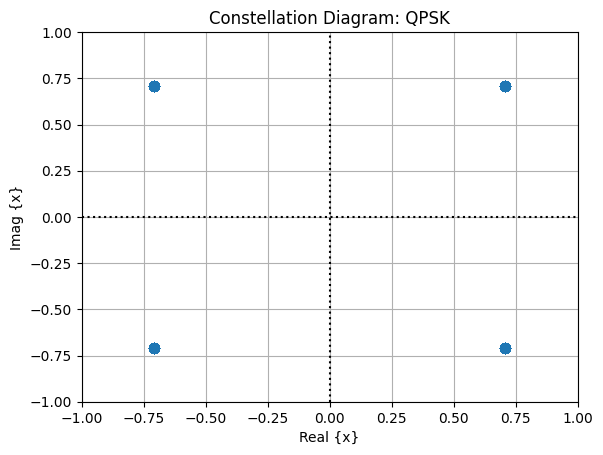
8. Constellation Diagram
[14]:
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.scatter(np.real(pbchSymbols), np.imag(pbchSymbols), s=48)
ax.axhline(y=0, ls=":", c="k")
ax.axvline(x=0, ls=":", c="k")
ax.set_xlim([-1,1])
ax.set_ylim([-1,1])
ax.set_xlabel("Real {x}")
ax.set_ylabel("Imag {x}")
ax.set_title("Constellation Diagram: QPSK")
ax.grid()
plt.show()
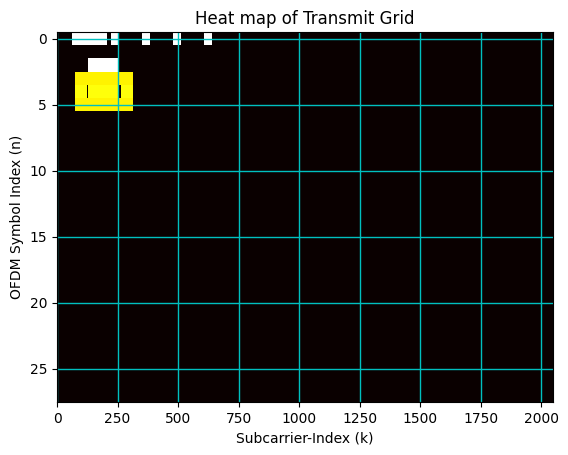
8. OFDM Modulation: Tx
[15]:
## Loading SSB to Resource Grid
numofGuardCarriers = (int((fftSize - Neff)/2), int((fftSize - Neff)/2))
offsetToPointA = 0
firstSCIndex = int(numofGuardCarriers[0] + offsetToPointA)
numOFDMSymbols = ssbGrid.shape[0]
X = np.zeros((numOFDMSymbols, fftSize), dtype= np.complex64)
X2 = np.zeros((numOFDMSymbols, fftSize), dtype= np.complex64)
X[:, firstSCIndex:firstSCIndex+ssbGrid.shape[-1]] = resourceGrid
X = np.concatenate([X, X2], axis = 0)
#__________________________________________________
## OFDM Modulation at Transmitter
#####################################
modulator = OFDMModulator(lengthCP[1])
x_time = modulator(X).flatten()
#______________________________________________________
# Plot Resource Grid
#################################################################
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
plt.imshow(np.abs(X), cmap = 'hot', interpolation='nearest', aspect = "auto")
ax = plt.gca();
ax.grid(color='c', linestyle='-', linewidth=1)
ax.set_xlabel("Subcarrier-Index (k)")
ax.set_ylabel("OFDM Symbol Index (n)")
ax.set_title("Heat map of Transmit Grid")
# Gridlines based on minor ticks
plt.show()
8. SDR-Setup Configurations
[16]:
# Basic SDR Setup
sdr = adi.Pluto("ip:192.168.3.1")
sdr.sample_rate = int(sample_rate)
# Config Tx
sdr.tx_rf_bandwidth = int(sample_rate) # filter cutoff, just set it to the same as sample rate
sdr.tx_lo = int(center_frequency)
sdr.tx_hardwaregain_chan0 = -30 # Increase to increase tx power, valid range is -90 to 0 dB
# Config Rx
sdr.gain_control_mode_chan0 = 'slow_attack'
# sdr.rx_hardwaregain_chan0 = 40.0 # dB
# The receive gain on the Pluto has a range from 0 to 74.5 dB.
# sdr.gain_control_mode_chan0 = 'slow_attack'
# # AGC modes:
# # 1. "manual"
# # 2. "slow_attack"
# # 3. "fast_attack"
sdr.rx_lo = int(center_frequency)
sdr.rx_rf_bandwidth = int(60*10**6) # filter width, just set it to the same as sample rate for now
sdr.rx_buffer_size = int(4*buffer_size)
8. Transmission: SDR RF Transmitter
[17]:
sdr.tx_destroy_buffer()
# Start the transmitter
sdr.tx_cyclic_buffer = True # Enable cyclic buffers
# sdr.tx_cyclic_buffer = False # Enable cyclic buffers
sdr.tx(1.3*2**17*(x_time.repeat(1))) # start transmitting
8. Receiver Implementation
8. Reception: SDR RF Receiver
[18]:
# Clear buffer just to be safe
for i in range (0, 10):
raw_data = sdr.rx()
# Receive samples
rx_samples = sdr.rx()
# # Stop transmitting
# sdr.tx_destroy_buffer()
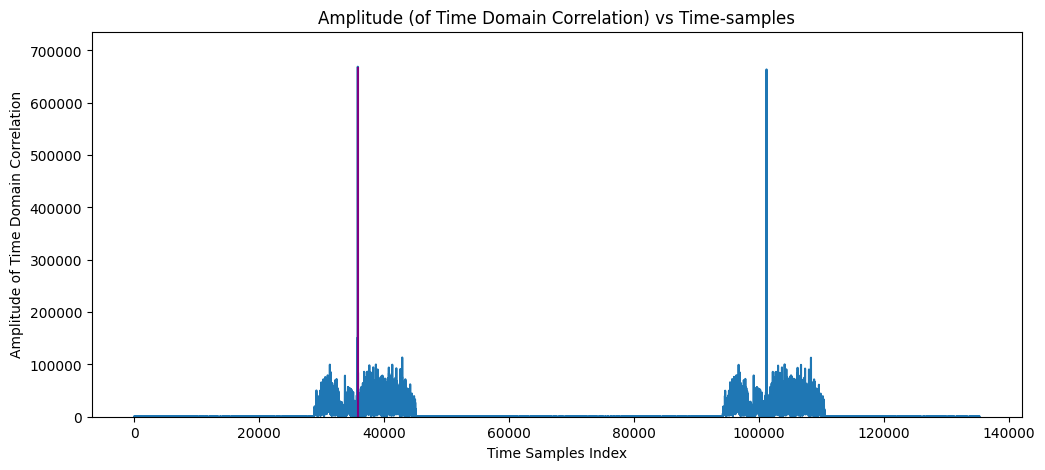
8. Time Synchronization: Based on PSS Correlation
[19]:
## PSS Detection: Based on time domain PSS Correlation
# pssPeakIndices, pssCorrelation, rN_ID2 = pssDetection(r, Nfft, lengthCP = lengthCP[1],
# N_ID2 = None, freqOffset = ssboffset,
# height = 0.75, prominence = 0.65, width=10)
## PSS Detection: Based on time domain PSS Correlation
# pssDetection = PSSDetection("correlation", "threshold")
pssDetection = PSSDetection("largestPeak")
ssboffset = int((fftSize-Neff)/2+ssbRGobject.startingSubcarrierIndices)
pssPeakIndices, pssCorrelation, rN_ID2, freqOffset = pssDetection(rx_samples, fftSize, lengthCP = lengthCP[1],
nID2=None, freqOffset = ssboffset)
if(pssPeakIndices > rx_samples.size - 28*(fftSize + lengthCP[1])):
pssPeakIndices = pssPeakIndices - 28*(fftSize + lengthCP[1])
## PSS Detection Plot
#################################################################
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(12, 5))
# single line
ax.plot(pssCorrelation)
ax.vlines(x = pssPeakIndices, ymin = 0*pssCorrelation[pssPeakIndices],
ymax = pssCorrelation[pssPeakIndices], colors = 'purple')
ax.set_ylim([0,np.max(pssCorrelation)*1.1])
ax.set_xlabel("Time Samples Index")
ax.set_ylabel("Amplitude of Time Domain Correlation")
ax.set_title("Amplitude (of Time Domain Correlation) vs Time-samples")
plt.show()
#________________________________________________________________
**(rasterOffset, PSS-ID) (74, 0)
**(rasterOffset, PSS-ID) (74, 1)
**(rasterOffset, PSS-ID) (74, 2)
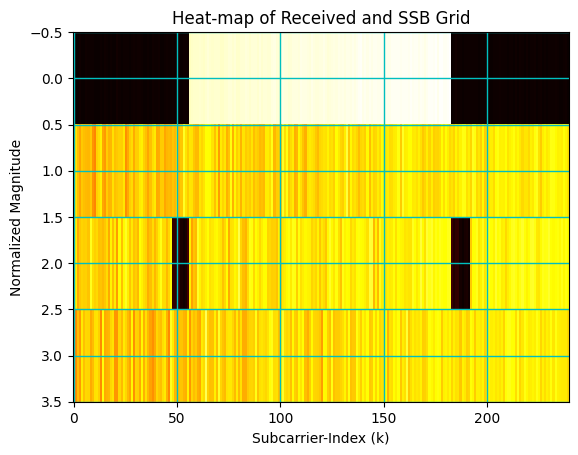
8. OFDM Demodulation and SSB Extraction
[20]:
## OFDM Demodulator Object
ofdmDemodulator = OFDMDemodulator(fftSize, lengthCP[1])
pssStartIndex = pssPeakIndices
# pssStartIndex = pssPeakIndices[0][0]
rxGrid = ofdmDemodulator((rx_samples.reshape(1,-1))[...,pssStartIndex:(pssStartIndex+4*(fftSize+lengthCP[1]))])
ssbSCSoffset = int((fftSize-Neff)/2+ssbRGobject.startingSubcarrierIndices)
ssbEstimate = rxGrid[:,:,ssbSCSoffset:(ssbSCSoffset+240)]
# Plot SSB
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
plt.imshow(np.abs(ssbEstimate[0]), cmap = 'hot', interpolation='nearest', aspect = "auto")
ax = plt.gca();
ax.grid(color='c', linestyle='-', linewidth=1)
ax.set_xlabel("Subcarrier-Index (k)")
ax.set_ylabel("Normalized Magnitude")
ax.set_title("Heat-map of Received and SSB Grid")
plt.show()
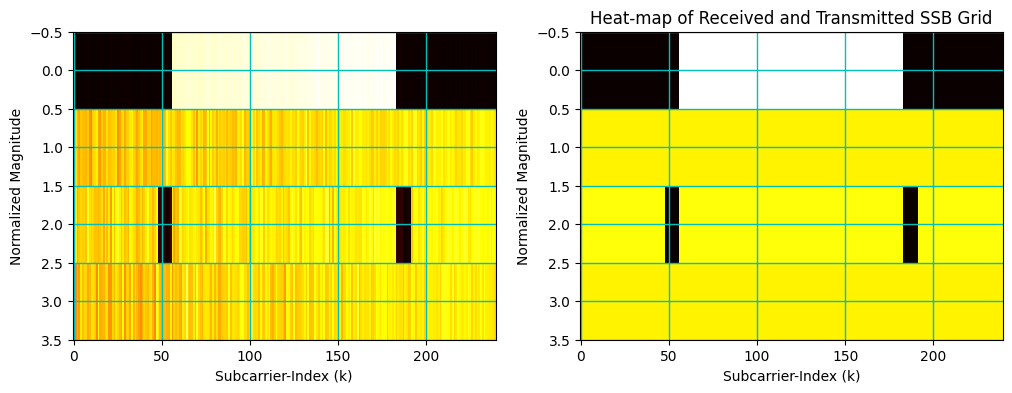
8. SSB Grid: Transmitter and Receiver
[21]:
# Plot SSB
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1,2, figsize=(12, 4))
ax[0].imshow(np.abs(ssbEstimate[0]), cmap = 'hot', interpolation='nearest', aspect = "auto")
ax[0].grid(color='c', linestyle='-', linewidth=1)
ax[0].set_xlabel("Subcarrier-Index (k)")
ax[0].set_ylabel("Normalized Magnitude")
ax[1].imshow(np.abs(ssb[0]), cmap = 'hot', interpolation='nearest', aspect = "auto")
ax[1].grid(color='c', linestyle='-', linewidth=1)
ax[1].set_xlabel("Subcarrier-Index (k)")
ax[1].set_ylabel("Normalized Magnitude")
plt.title("Heat-map of Received and Transmitted SSB Grid")
plt.show()
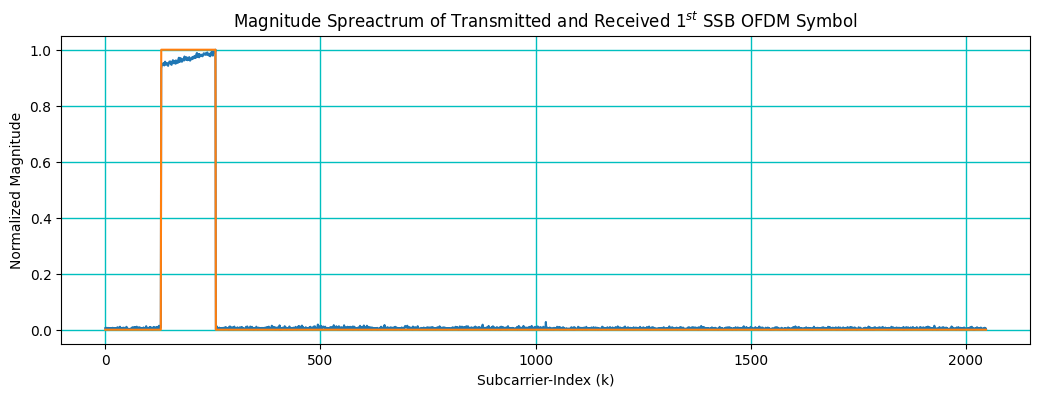
8. Spectrum: Transmitted Grid and Received Grid
[22]:
# Plot SSB
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(12.5, 4))
ax.plot(np.abs(rxGrid[0][0])/np.abs(rxGrid[0][0]).max())
ax.plot(np.abs(X[2])/np.abs(X[2]).max())
ax.grid(color='c', linestyle='-', linewidth=1)
ax.set_xlabel("Subcarrier-Index (k)")
ax.set_ylabel("Normalized Magnitude")
ax.set_title("Magnitude Spreactrum of Transmitted and Received $1^{st}$ SSB OFDM Symbol")
plt.show()
8. Parameter Estimation for SSB and PBCH
[23]:
## N_ID_1 Estimation: SSS based
sssDetection = SSSDetection(method="channelAssisted", nID2=rN_ID2)
rN_ID1 = sssDetection(ssbEstimate[0])
rN_ID = 3*rN_ID1 + rN_ID2
## Generate SSB object to get DMRS and PBCH Indices
rxSSBobject = SSB_Grid(rN_ID)
rxDMRSIndices = rxSSBobject.dmrsIndices
## Generate DMRS sequence
dmrsDetection = DMRSParameterDetection(int(rN_ID), nssbCandidatesInHrf)
rssbIndex, rHrfBit = dmrsDetection(ssbEstimate[0])
rxDMRSobject = DMRS("PBCH", int(rN_ID), int(rssbIndex), nssbCandidatesInHrf, rHrfBit)
rxDMRSseq = rxDMRSobject(dmrsLen)
8. Channel Estimation and PBCH Symbol Equalization
[24]:
# ## Estimating the channel at DMRS (t-f) location, interpolting for data (t-f) location and equalizing the symbols
# ## Object for Channel Estimation
# chanEst = ChannelEstimationAndEqualization(estimatorType = "ZF", interpolatorType = "NN")
# rxPBCHIndices = rxSSBobject.pbchIndices
# pbchEstimate = chanEst(ssbEstimate, rxDMRSseq, rxDMRSIndices, rxPBCHIndices, 10)
chanEst = ChannelEstimationAndEqualizationPBCH(estimatorType = "ZF", interpolatorType = "Linear", isUEmobile=True)
pbchEstimate = chanEst(ssbEstimate, rxDMRSseq, rN_ID)
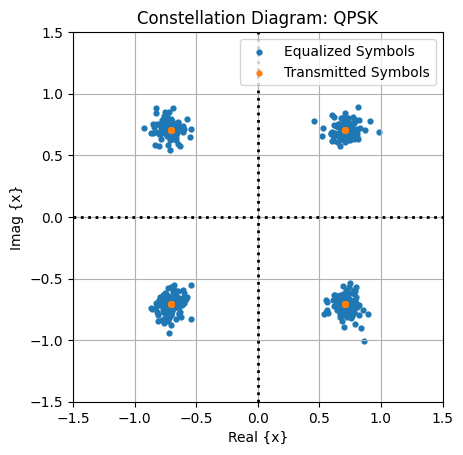
8. PBCH Decoding and Constellation
[25]:
## PBCH Chain for Decoding information
polarDecoder = "SCL"
symbolDemapper = "maxlog"
# extractMIBinfo = False
extractMIBinfo = True
# carrierFreq, cellID, nssbCandidatesInHrf, ssbIndex, polarDecType, symbolDemapperType
pbchDecoder = PBCHDecoder(center_frequency, int(rN_ID), nssbCandidatesInHrf, rssbIndex, polarDecoder, symbolDemapper)
rxMIB, check = pbchDecoder(pbchEstimate, 10, extractMIBinfo)
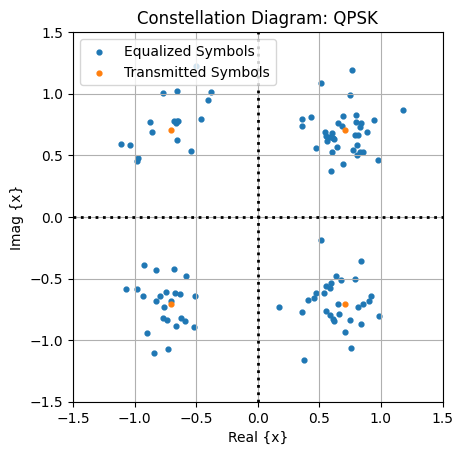
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.set_aspect(True)
ax.scatter(np.real(pbchEstimate), np.imag(pbchEstimate), s = 12, label = "Equalized Symbols")
ax.scatter(np.real(pbchSymbols), np.imag(pbchSymbols), s = 12, label = "Transmitted Symbols")
ax.grid()
ax.axhline(y=0, ls=":", c="k", lw = 2)
ax.axvline(x=0, ls=":", c="k", lw = 2)
ax.set_xlim([-1.5,1.5])
ax.set_ylim([-1.5,1.5])
ax.set_xlabel("Real {x}")
ax.set_ylabel("Imag {x}")
ax.set_title("Constellation Diagram: QPSK")
ax.legend(loc = "best")
plt.show()
C:\Users\asnat\Downloads\May4\May4\toolkit5G\ChannelCoder\PolarCoder\polarDecoder.py:494: UserWarning: Required ressource allocation is large for the selected blocklength. Consider option `cpu_only=True`.
warnings.warn("Required ressource allocation is large " \
[26]:
check
[26]:
array([[ True]])
[27]:
pbchDecoder.mibRx.displayParameters(0)
Carrier Frequency: 2000000000.0
ChoiceBit: 1
nSsbCandidatesInHrf: 4
subCarrierSpacingCommon:15000
DMRSTypeAPosition: typeA
controlResourceSet0: 10
searchSpace0: 7
cellBarred: barred
intraFreqReselection: allowed
systemFrameNumber: 528
ssbSubCarrierOffset: 10
HRFBit: 0
iSSBindex: 0
[28]:
pbchObject.mib.displayParameters(0)
Carrier Frequency: 2000000000.0
ChoiceBit: 1
nSsbCandidatesInHrf: 4
subCarrierSpacingCommon:15000
DMRSTypeAPosition: typeA
controlResourceSet0: 10
searchSpace0: 7
cellBarred: barred
intraFreqReselection: allowed
systemFrameNumber: 528
ssbSubCarrierOffset: 10
HRFBit: 0
iSSBindex: 0
8. Performance Verification
[29]:
if (rN_ID == N_ID):
print("[Success]: Cell-IDs correctly detected!")
else:
if (rN_ID1 != N_ID1 and rN_ID2 != N_ID2):
print("[Failed]: Receiver couldn't detect the Cell-ID1 and cell-ID2 correctly!")
elif(rN_ID1 != N_ID1):
print("[Failed]: Receiver couldn't detect the Cell-ID1 correctly!")
else:
print("[Failed]: Receiver couldn't detect the cell-ID2 correctly!")
if (rssbIndex == ssbIndex[0]):
print("[Success]: DMRS parameters correctly detected!")
else:
print("[Failed]: Receiver couldn't detect the ssbIndex correctly!")
## Computing BER: Coded and Uncoded
numUEs = 1
nBatch = 1
uncodedBER = np.zeros((numUEs, nBatch))
codedBER = np.zeros((numUEs, nBatch))
bitEst = pbchDecoder.llr.copy()
bitEst[pbchDecoder.llr > 0] = 1
bitEst[pbchDecoder.llr < 0] = 0
uncodedBER = np.mean(np.abs(bitEst - pbchObject.scr2bits[0]))
codedBER = np.mean(np.abs(pbchDecoder.pbchDeInterleavedBits - pbchObject.mibSequence[0]))
print(" (uncoded-BER, codedBER): "+str((uncodedBER, codedBER)))
[Success]: Cell-IDs correctly detected!
[Success]: DMRS parameters correctly detected!
(uncoded-BER, codedBER): (0.0, 0.0)
[30]:
ofdmDemodulator = OFDMDemodulator(fftSize, lengthCP[1])
startSampleIndex = pssPeakIndices - 2*(fftSize + lengthCP[1])
# pssStartIndex = pssPeakIndices[0][0]
rxResGrid = ofdmDemodulator((rx_samples.reshape(1,-1))[...,startSampleIndex:(startSampleIndex+14*(fftSize+lengthCP[1]))])
rxGrid = rxResGrid[0,:,firstSCIndex:firstSCIndex+Neff]
[31]:
rxResGrid.shape
[31]:
(1, 14, 2048)
[32]:
# Plot Resource Grid
#################################################################
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
plt.imshow(np.abs(rxGrid), cmap = 'hot', interpolation='nearest', aspect = "auto")
ax = plt.gca();
ax.grid(color='c', linestyle='-', linewidth=1)
ax.set_xlabel("Subcarrier-Index (k)")
ax.set_ylabel("OFDM Symbol Index (n)")
ax.set_title("Heat map of Transmit Grid")
# Gridlines based on minor ticks
plt.show()
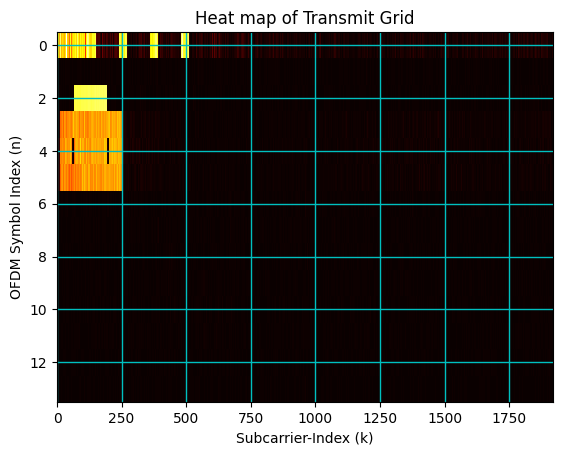
8. Channel Estimation and Equalization of PDCCH
[33]:
rxPDCCHGrid = np.zeros((14,270*12), dtype = np.complex64)
rxPDCCHGrid[:,0:Neff] = rxGrid
[34]:
##### Channel Estimation and Equalization #####
snr = 10
channelEst = ChannelEstimationAndEqualizationPDCCH(duration, frequencyDomainResources, monitoringSymbolsWithinSlot)
equalized_Sym = channelEst(rxPDCCHGrid[np.newaxis], cce_reg_Mapping, L, R, nshift,slotNumber, N_ID)
equalizedGrid = rxPDCCHGrid[np.newaxis]/channelEst.Hest
8. Blind Decoding of PDCCH candidates
[35]:
#########################
# Intiate Blind Decoding
#########################
bdObj = PDCCHCandidateBlindDecoding(coresetPRBIndices, duration, startSymIndex, ssType, AggLevel ,ueCand)
bdObj(equalizedGrid, K, E, snr, RNTI,N_ID, decoderType="SC", demappingMethod="app")
print("##########################################################################")
print()
Warning: 5G Polar codes use an integrated CRC that cannot be materialized with SC decoding and, thus, causes a degraded performance. Please consider SCL decoding instead.
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Checking the CRC:
[[ True]]
Blind Decoding Successful for the CCE Indices [0 1]..!
##########################################################################
8. Received Constellation
[36]:
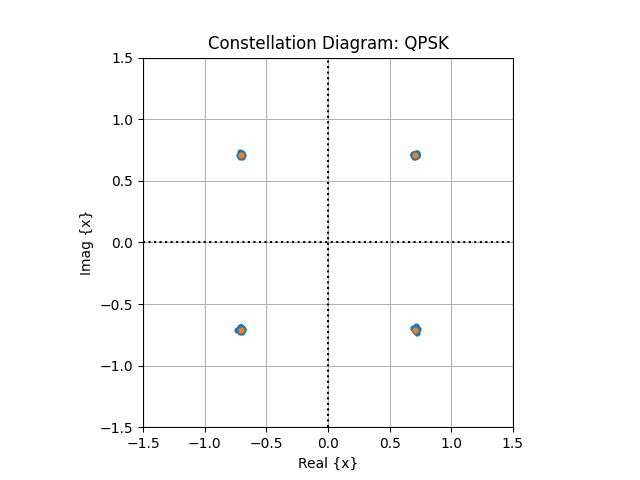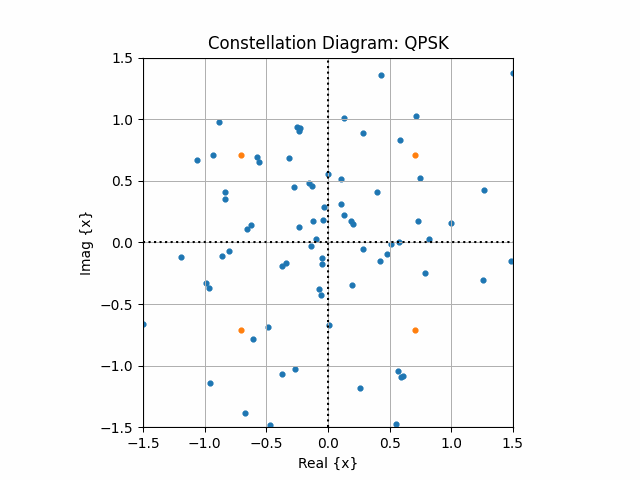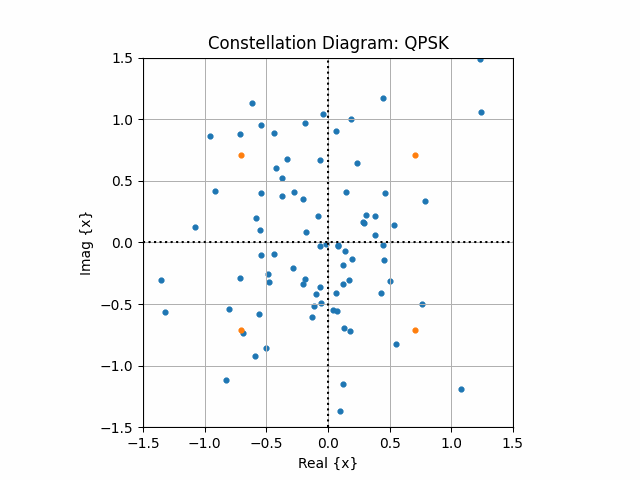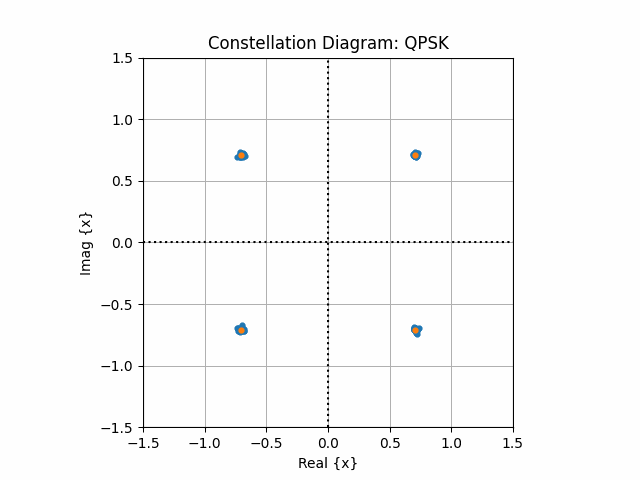
pdcchSymbols = np.array([1+1j,1-1j,-1-1j,-1+1j])/np.sqrt(2)
## PBCH Chain for Decoding information
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.set_aspect(True)
ax.scatter(np.real(bdObj.equalizedDataSym), np.imag(bdObj.equalizedDataSym), s = 12, label = "Equalized Symbols")
ax.scatter(np.real(pdcchSymbols), np.imag(pdcchSymbols), s = 12, label = "Transmitted Symbols")
ax.grid()
ax.axhline(y=0, ls=":", c="k", lw = 2)
ax.axvline(x=0, ls=":", c="k", lw = 2)
ax.set_xlim([-1.5,1.5])
ax.set_ylim([-1.5,1.5])
ax.set_xlabel("Real {x}")
ax.set_ylabel("Imag {x}")
ax.set_title("Constellation Diagram: QPSK")
ax.legend(loc = "best")
plt.show()
8. Quasi real time animation
[37]:
# function that draws each frame of the animation
qpskSymbols = np.array([1+1j,1-1j,-1-1j,-1+1j])/np.sqrt(2)
def animate(i):
# Receive samples
rx_samples = sdr.rx()
pssPeakIndices, pssCorrelation, rN_ID2, freqOffset = pssDetection(rx_samples, fftSize, lengthCP = lengthCP[1],
nID2=None, freqOffset = ssboffset)
if(pssPeakIndices < 3*(fftSize + lengthCP[1])):
pssPeakIndices = pssPeakIndices + 14*(fftSize + lengthCP[1])
elif(pssPeakIndices > rx_samples.size - 13*(fftSize + lengthCP[1])):
pssPeakIndices = pssPeakIndices - 14*(fftSize + lengthCP[1])
# # CFO estimation
# obj = CarrierFrequencyOffsetEstimation(fftSize,lengthCP[1])
# cfoEst = obj(rx_samples[pssPeakIndices: pssPeakIndices + numSamples],numCFOIteration = 2) # Computed CFO
## OFDM Demodulator Object
ofdmDemodulator = OFDMDemodulator(fftSize, lengthCP[1])
startSampleIndex = pssPeakIndices - 2*(fftSize + lengthCP[1])
# pssStartIndex = pssPeakIndices[0][0]
rxResGrid = ofdmDemodulator((rx_samples.reshape(1,-1))[...,startSampleIndex:(startSampleIndex+14*(fftSize+lengthCP[1]))])
rxGrid = rxResGrid[0,:,firstSCIndex:firstSCIndex+Neff]
rxPDCCHGrid = np.zeros((14,270*12), dtype = np.complex64)
rxPDCCHGrid[:,0:Neff] = rxGrid
##### Channel Estimation and Equalization #####
snr = 10
channelEst = ChannelEstimationAndEqualizationPDCCH(duration, frequencyDomainResources, monitoringSymbolsWithinSlot)
equalized_Sym = channelEst(rxPDCCHGrid[np.newaxis], cce_reg_Mapping, L, R, nshift,slotNumber, N_ID)
equalizedGrid = rxPDCCHGrid[np.newaxis]/channelEst.Hest
## Blind Decoding
bdObj = PDCCHCandidateBlindDecoding(coresetPRBIndices, duration, startSymIndex,
ssType, AggLevel ,ueCand, False)
rdciBits = bdObj(equalizedGrid, K, E, snr, RNTI,N_ID, decoderType="SC", demappingMethod="app")
ax.clear()
ax.set_xlim([-1.5, 1.5])
ax.set_ylim([-1.5, 1.5])
ax.scatter(np.real(bdObj.equalizedDataSym), np.imag(bdObj.equalizedDataSym), s = 12, label = "Equalized Symbols")
ax.scatter(np.real(qpskSymbols), np.imag(qpskSymbols), s = 12, label = "Transmitted Symbols")
ax.grid()
ax.axhline(y=0, ls=":", c="k")
ax.axvline(x=0, ls=":", c="k")
ax.set_xlabel("Real {x}")
ax.set_ylabel("Imag {x}")
ax.set_title("Constellation Diagram: QPSK")
# Plot SSB
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.set_aspect(True)
scale = 100
#####################
# run the animation
#####################
# frames= 20 means 20 times the animation function is called.
# interval=500 means 500 milliseconds between each frame.
# repeat=False means that after all the frames are drawn, the animation will not repeat.
# Note: plt.show() line is always called after the FuncAnimation line.
anim = animation.FuncAnimation(fig, animate, frames=1000, interval=1, repeat=False, blit=True)
# saving to mp4 using ffmpeg writer
plt.show()
anim.save("PDCCH_Constellation.gif", fps = 10)
# writervideo = animation.FFMpegWriter(fps=60)
# anim.save('Overall.mp4', writer=writervideo)
[ ]: